Table of Contents
Reading SAMCEF files
Introduction
![]() Due to historical reasons, the preprocessor of SAMCEF (called BACON) can be used to generate a mesh and geometrical entities. The module
Due to historical reasons, the preprocessor of SAMCEF (called BACON) can be used to generate a mesh and geometrical entities. The module toolbox.samcef defines functions that convert a .fdb file (fdb stands for “formatted database”) to commands that Metafor understands. If a .dat file (i.e. a BACON script file) is provided, Metafor automatically runs BACON first as a background process in order to create the missing .fdb file. In this case, a SAMCEF license is required.
BACON ''.dat'' file
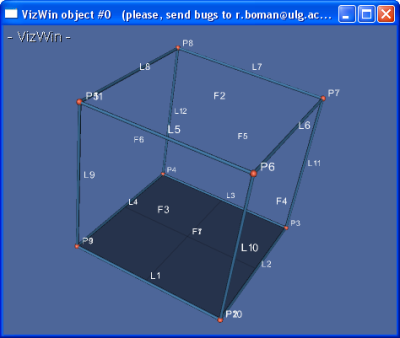
The example simulation consists of a sheared cube (lower and upper faces and fixed and moved one with respect to another). The figure below shows the geometry:
The BACON input file named cubeCG.dat (located in apps/ale) contains the commands used to create the geometry, the mesh and node groups (selections).
Geometry
The geometry is created with the following BACON commands (see BACON manual for details):
.3POIfor the 8 points..3DROfor the 12 edges..CONfor the 6 wires..FACEfor the 6 sides..PLANto create a surface (required for the 2D domain, see below)..VPEAUfor the skin..DOMfor the domain (one 3D domain - the cube - and one 2D domain - the lower side which will be meshed and extruded).
Mesh Generation
- Performed with
.GEN. - Lines are meshed with the command “
MODIFIE LIGNE”. - The lower side is meshed with a transfinite mapping (command “
transfini”) and extruded with the command “EXTRUSION”. - An attribute number must then be defined.
Choice of Element Type
- The command
.HYP VOLUMEis used (in 2D and 3D).
Definition of node/element groups (selections)
- The command
.SELis used - If
.RENis used to change the numbering of nodes and mesh elements, it should be done before the.SEL. - Node selections will be used to define boundary conditions (fixations, contact, …) in the Metafor model.
Manual Creation of the .fdb file
BACON can be started manually with the command:
samcef ba aleCubeCg n 1
From the .dat file, a .fdb is created with BACON with the commands:
INPUT .SAUVE DB FORMAT .STO
Summary: What can be imported from BACON?
- Points
- Curves:
Line-Arc(points generated automatically with a negative numbed in Metafor are shifted (numPoint = numMaxPoints-numPoint) - Surface:
Plan-Ruled-Coons(Only planes defined using three numbers are imported (other planes generate cpoints outside db) ). - Wire
- Sides: Imported (even if not treated by Bacon)
- Skins: If
MultiProjSkinobjects are created, it is best to create them in the Python data set. - Nodes: (imported as
MeshedPoints) - Mesh elements: Triangle - Quad - Tetra - Hexa (with recovery in Metafor)
- Selections: only groups of nodes are imported (other have no use in Metafor)
- “DAO – Mesh” relations are not read again (
nodeOnLine, …)
Metafor input file
Reading the BACON file from Metafor
In Metafor, the file .dat is converted thanks to a conversion module named toolbox.samcef (see apps.ale.cubeCG):
import toolbox.samcef bi = toolbox.samcef.BaconImporter(domain, os.path.splitext(__file__)[0]+'.dat' ) bi.execute()
where domain is the domain that should be filled with the converted mesh and geometry. The second argument corresponds to the full path to the file cubeCG.dat (it is computed from the full path of the python input file).
If all goes well, a file cubeCG.fdb is then created in the folder workspace/apps_ale_cubeCG
Element Generation in Metafor
The BACON attributes are converted to Groups in Metafor. For example, if attribute #99 has been used when generating mesh in BACON, all the elements are stored in groupset(99) in Metafor.
app = FieldApplicator(1) app.push(groupset(99)) interactionset.add(app)
Boundary conditions in Metafor
Selections in BACON are translated into Groups with the same number. Boundary conditions such as prescribed displacements or contact can be thus defined easily in Metafor. For example, a selection such as .SEL GROUPE 4 NOEUDS can lead to the following command in the input file:
loadingset.define(groupset(4), Field1D(TX,RE))