This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
Surfaces
Definition
The surface is the basic 3D geometric entity. At this level, the geometric concept, Surface, is separated from the topological one, (Side). This allows a definition of a surface much larger than the face (analytically, surfaces are usually infinite – cylinders, planes, NURBS, …), and then to restrain them with a Wire.
Plane
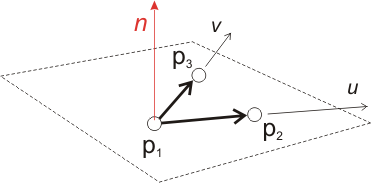
A plane is defined by three points:
plane = surfaceset.add( Plane(number, p1, p2, p3) )
Its normal (and therefore the surface orientation) is calculated using the cross product of the vectors:
$\boldsymbol{p_2}-\boldsymbol{p_1}$ et $\boldsymbol{p_3}-\boldsymbol{p_1}$.
p1, p2, p3 | reference towards the Points |
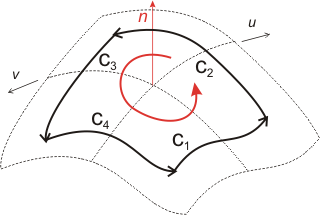
Coons
A Coons is a linear interpolation between four curves. This curves are gathered in a close wire. The wire orientation defines the surface orientation.
coons = surfaceset.add( Coons(number, wire) )
wire | reference towards the Wire |
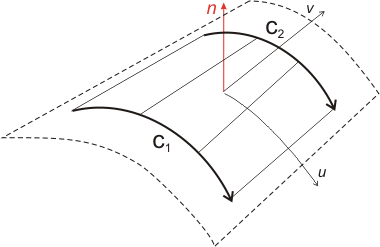
Ruled Surface
A ruled surface is defined by linearly interpolating the space between two curves. The orientation of these curves sets the surface orientation.
ruled = surfaceset.add( Ruled(number, curve1, curve2) )
curve1, curve2, … | references towards the Curves |
Ruled surfaces can be used to create planes, if the two curves are lines, or cylinders if the curves are arcs.
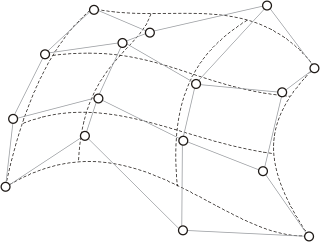
Nurbs
nur = surfaceset.add( NurbsSurface(number) ) nur.setDegreeU(degU) nur.setDegreeV(degV) nur.push(i1,j1,p1); nur.pushWeight(i1,j1,w1) nur.push(i2, j2, p2); nur.pushWeight(i2, j2, w2) nur.pushKnotU(knotu1) ... nur.pushKnotU(knotu2) nur.pushKnotV(knotv1) ... nur.pushKnotV(knotv2)
degU, degV | degree along U and V |
i1, j1, i2, j2, … | indices of the pole matrix |
p1, p2, … | reference towards the points (poles) |
w1, w2, … | weights |
knotu1, knotu2, … | knot vector along U |
knotv1, knotv2, … | knot vector along V |
Surface of revolution
revsur = surfaceset.add( RevolutionSurface(number, axe, wire) )
where
axe | Line which defines the revolution axis |
wire | Wire which will rotate along tje revolution axis (it cannot touch the axis on its first point and must be coplanar with it). |
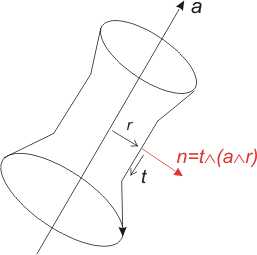
Cylinder
c = Cylinder(number, axe, radius, ptGen) #First way to use Cylinder c = Cylinder(number, axe, radius) #Second way to use Cylinder c.setProjType(projType) surfaceset.add( c )
where
axe | Line which defines the cylinder axis | |
radius | cylinder radius | |
ptGen | optional 'Point of the generating line of the cylinder. This point must be situated: WARNING_MESSAGE (see apps.qs.contactCylProj0Point). This point is compulsory if the cylinder has a given rotation. |
| projType'' | = 0 : the surface is finite and limited by the length of the axis = 1 : the surface is infinite |